Table of Contents
- Introduction
- Key Activated Carbon Specifications for Performance
- Surface Area (BET)
- Porosity and Pore Structure
- Surface Chemical Properties
- Mechanical Strength
- Adsorption Performance
- Catalytic Performance
- HANYAN Laboratory Test Service
- Conclusion
Introduction
Activated carbon is a versatile material used in air and water purification, chemical recovery, catalysis, and more. Its performance depends heavily on specific physical and chemical characteristics. For engineers, researchers, and procurement specialists, understanding the key performance indicators (KPIs) of activated carbon is crucial for selecting the right product for each application. This article outlines the six most important metrics used to evaluate activated carbon quality.
Key Activated Carbon Specifications for Performance
1. Surface Area (BET)
The BET surface area measures the total surface available for adsorption per gram of activated carbon, typically expressed in m²/g.
- Why it matters: A higher surface area usually translates to better adsorption capacity.
- Application examples: Water and air purification, where higher surface contact improves pollutant capture.
🔍 Industry benchmark: High-performance activated carbon often exceeds 1000 m²/g.
2. Porosity and Pore Structure
Porosity refers to the pore volume and distribution within the activated carbon.
- Micropores (<2 nm): Best for small molecule gases like CO₂.
- Mesopores (2–50 nm): Important for medium-sized molecules such as VOCs.
- Macropores (>50 nm): Enhance diffusion and transport efficiency.
- Why it matters: Tailored pore structures allow activated carbon to target specific contaminants more effectively.
3. Surface Chemical Properties
Surface chemistry includes the functional groups (e.g., hydroxyl, carboxyl, carbonyl) present on the carbon surface.
- Impact: These groups influence adsorption through chemical interactions.
- Enhanced functionality: Modified activated carbon can improve affinity for specific pollutants (e.g., mercury, formaldehyde).
🎯 Pro tip: Surface oxidation or chemical treatments can customize adsorption behavior for specialized uses.
4. Mechanical Strength
Mechanical strength measures the hardness and durability of activated carbon particles.
- Why it matters: Stronger carbon resists crushing and attrition during use and regeneration cycles.
- Critical in: Packed bed filters, fluidized beds, and high-flow systems.
💡 Best practice: Choose high-strength activated carbon for long-term or regenerable applications.
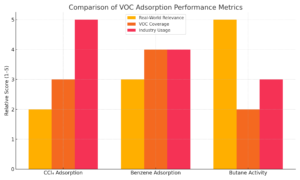
5. Adsorption Performance
This is the core functional property—how well activated carbon removes contaminants.
- Measured by:
- CTC (Carbon Tetrachloride) value: Gas-phase adsorption test
- Iodine number: Liquid-phase adsorption test
- Why it matters: Reflects real-world efficiency in capturing pollutants.
📌 Tip: Look for application-specific values—air filters need high CTC, while water filters benefit from high iodine numbers.
6. Catalytic Performance
Some activated carbons are engineered to act as catalysts or catalyst supports.
- Used in:
- Decomposition of ozone, chlorine, or sulfur compounds
- Support for metal catalysts in chemical reactions
- Why it matters: Adds multifunctionality, especially in industrial gas treatment.
⚗️ Advanced application: Catalytic carbons can reduce the need for additional reagents or steps in a purification process.
HANYAN Laboratory Test Service
HANYAN, while monitoring product shipments, also provides customers with accurate and reliable product testing data. This not only saves customers significant financial, material, and human resources but, more importantly, ensures that they can pursue market expansion without any concerns. It guarantees that customers can use HANYAN’s products with confidence. Currently, the company has obtained international certifications such as ISO9001, HALAL, and KOSHER, as well as domestic health permits. Please click to check more details for HANYAN test service.
Conclusion
The performance of activated carbon is not defined by a single parameter but by a combination of surface area, pore size distribution, surface chemistry, strength, adsorption metrics, and sometimes catalytic properties. Understanding these key indicators allows professionals to choose the right carbon for the job—whether it’s odor control in HVAC, heavy metal removal from water, or solvent recovery in industrial emissions.
When sourcing activated carbon, always request a detailed technical datasheet (TDS) and assess it based on the metrics outlined above to ensure it meets your specific application needs.
Article Keywords: activated carbon performance indicators, BET surface area, adsorption capacity, activated carbon pore size, CTC value, iodine number, mechanical strength, catalytic activated carbon, surface chemistry adsorption, industrial carbon selection, high-efficiency activated carbon, activated carbon quality, adsorbent properties, carbon material selection.